Secretion Removal Techniques in People with Spinal Cord Injury through Physiotherapy
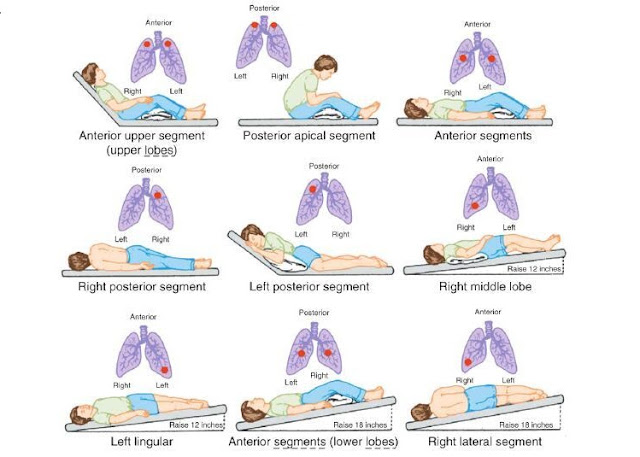
Respiratory complications are a leading cause of injury and mortality in people with spinal cord injury (SCI) and are more pronounced in individuals with higher level and complete injuries. A major contributor to respiratory illness in individuals with SCI is secretion retention, particularly among individuals with cervical lesions. Higher levels of SCI result in greater denervation of the ventilatory muscles thereby decreasing both inspiratory capacity and expiratory muscle force and resulting in an impaired cough. The figure shows the innervation of the respiratory muscles. Cervical SCI also denervates sympathetic pathways leading to a state of parasympathetic dominance that may increase mucus production and contribute to airway hyper responsiveness. A diminishing cough combined with mucus hyper secretion can overwhelm mucociliary clearance in people with SCI. The impact of SCI on normal airway clearance can be exemplified by examining the sequence of a cough. After f...