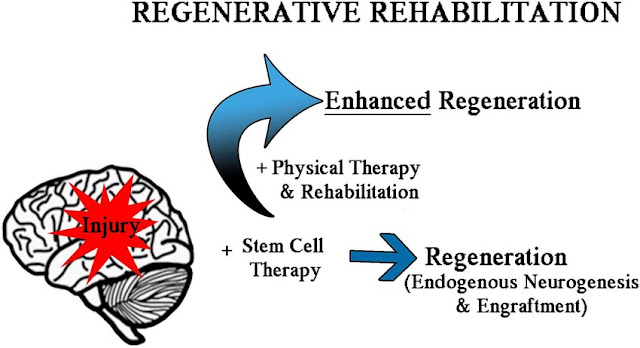
Regenerative Rehabilitation – a New Future?
Regenerative
medicine includes the "procedure of making living, useful
tissues to supplant or repair tissue or organ work lost because of infection,
age, harm, or inherent deformities". This new field holds the wonderful
certification of recovering tissues and organs in the body by either
supplanting hurt tissue or by propelling the body's own specific repair
segments to patch in advance miserable conditions. As regenerative medicine
turns out to be progressively coordinated into restorative practice, new
methodologies will address the main driver of sickness and offer already
unachievable prospects for tissue repair.
Regenerative medicine
generally draws from the field of transplantation prescription that together
with implantable medicinal gadgets has significantly adjusted the direction for
incessant patients experiencing end-organize organ failure. However,
transplantation medicine is limited by donor organ shortage. But, the gap
between available organ donation and recipients is rapidly widening Moreover,
recipients, although fortunate to receive donor organs, are placed at risk for
tissue rejection and must get long lasting immunosuppressive
medication
treatment with an expanded frequency of transplantation-related tumours.
Moreover, transplant difficulties are normal. Lung transplant recipients, for
example, experience the highest rates of re-hospitalization for transplant
complications, i.e., ~44 per 100 patients within the first year. Together,
these data indicate that transplantation needs far exceed supply, and even when
transplanted organs are available, patients face life-long challenges.
The emerging field of regenerative
medicine aims to address the unmet medical need for organ and tissue
replacement. Regenerative medicine covers an expansive range including
techniques for advancement of tissue engineering, self-healing, neo-organogenesis and cell-based
therapies. In fact, the world's first fruitful research facility developed
organ (a urinary bladder) was created from the patient's own particular cells,
molded by a bioreactor and in this manner carefully embedded again into the
patient. Long haul follow-up in patients treated by this regenerative method
showed change in bladder spill point weight, volume and consistence. This
confirmation of-idea innovation gives an early case of the up and coming period
of regenerative arrangements.
A wide array of
engineered organs (urinary bladder, trachea, and cornea) or tissues
(skin, cartilage, muscle) is developed to the point of clinical
applications. Many other regenerative technologies are under development in
preclinical stages prior to human trials.


Comments
Post a Comment